WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communications) is primarily known for its support for audio and video communications; however, it also supports data channels. This article explains more about this and shows you how to use the WebRTC data channel.
What is a WebRTC data channel?
WebRTC data channel is another channel in WebRTC other than video and audio. In the data channel, you can send any kind of information to other clients. Data channels can be utilized in various use cases including chat, control messages, or file sharing. Ant Media Server provides a generic data channel infrastructure that can be used in all use cases.
Enabling the WebRTC data channel
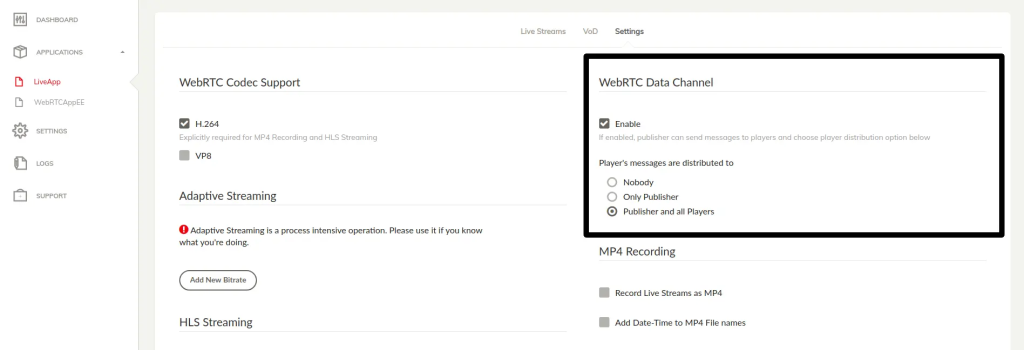
In order to use data channel functionality, you first should enable the WebRTC data channel in the dashboard, in order to send/receive anything through the data channel with SDKs.
There are some data delivery options for data channels you can choose:
- Nobody: Only the publisher can send messages to the players and players cannot send messages.
- Only publisher: Player messages are only delivered to the publisher. Publisher messages are delivered to all players.
- Publisher and all players: Players’ and publisher’s messages are delivered to the publisher and all other players who are watching the stream and publisher.
Sending and receiving messages with JavaScript
Sending and receiving messages via WebRTC data channels can be implemented using Ant Media Server Javascript SDK with less than 10 lines of code.
Sending a message
sendData = function(streamId, message) function in webrtc_adaptor.js is used to send messages as shown in the following code:
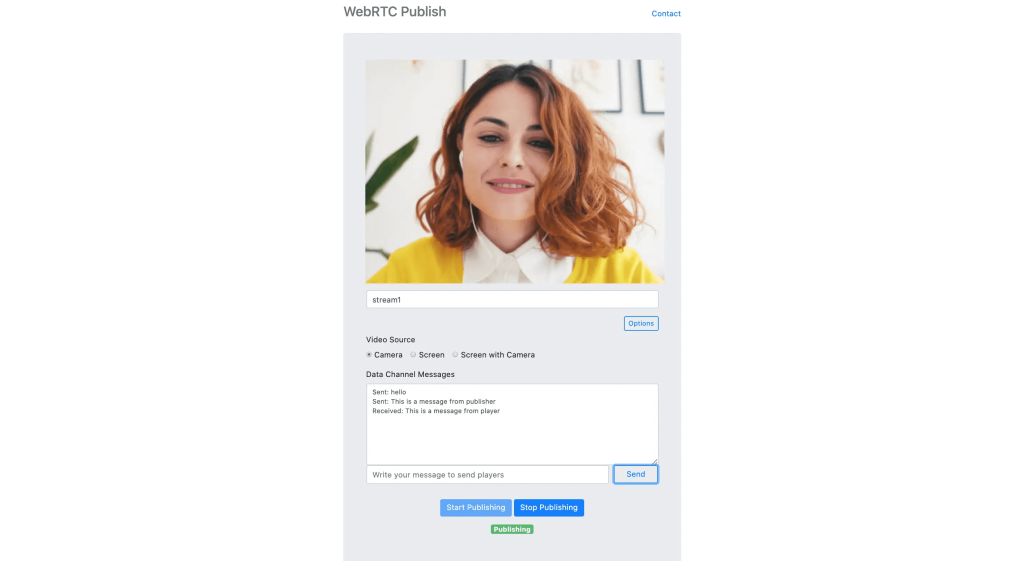
Here is a screenshot of the sample page that you can try in WebRTC publishing:
Receiving a message
In order to receive a message, just add the following callback for WebRTCAdaptor.
callback : function(info, description) {
if (info == "data_channel_opened") {
console.log("data channel is open");
}
else if (info == "data_received") {
console.log("Message received ", description.data );
handleData(description);
}
else if (info == "data_channel_error") {
handleError(description);
} else if (info == "data_channel_closed") {
console.log("Data channel closed " );
}
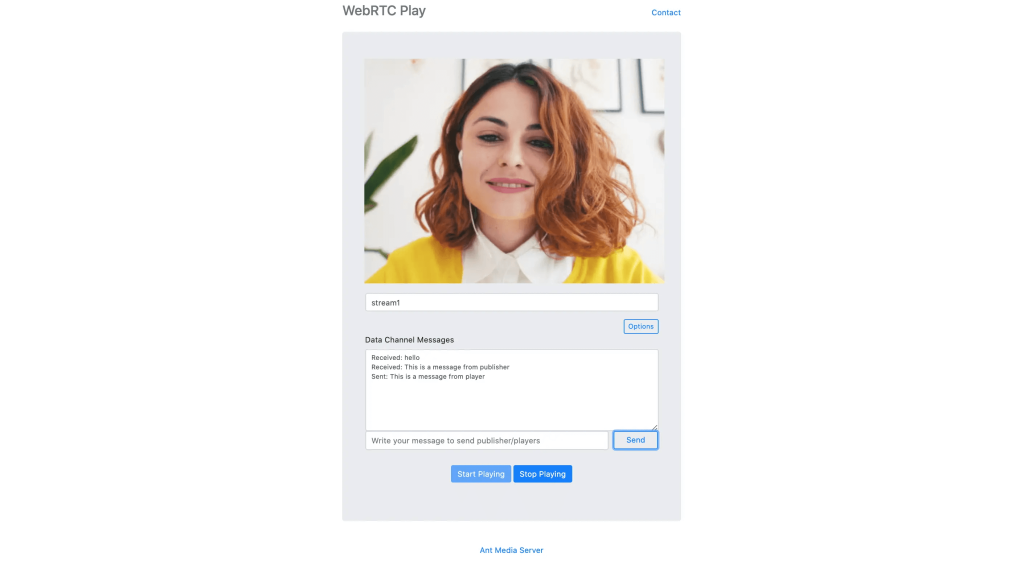
A basic sample for sending and receiving messages through the WebRTC data channel is available on WebRTC Publishing and Playing pages as shown above.
Sending & receiving data with Android SDK
Exchanging data through WebRTC data channels is also straightforward with AMS Android WebRTC SDK. Your activity should implement IDataChannelObserver interface as shown below:
public interface IDataChannelObserver {
/**
* Called by SDK when the buffered amount has been changed
*/
void onBufferedAmountChange(long previousAmount, String dataChannelLabel);
/**
* Called when the state of the data channel has been changed
*/
void onStateChange(DataChannel.State state, String dataChannelLabel);
/**
* Called by SDK when a new message is received
*/
void onMessage(DataChannel.Buffer buffer, String dataChannelLabel);
/**
* Called by SDK when the message is sent successfully
*/
void onMessageSent(DataChannel.Buffer buffer, boolean successful);
}Initialization
MainActivity.java sample code in Android SDK implements the IDataChannelObserver and has the required initialization code. The base data channel functionality is in the WebRTCClient.java, MainActivity file. The sample below shows how to init, send and receive data messages in Android SDK. In order to init the WebRTCClient Before initialization of WebRTCClient you also need to add the following lines in onCreate method of the Activity.
Sending data
WebRTClient has sendMessageViaDataChannel(DataChannel.Buffer) method to send messages. It has also been called in MainActivity as follows.
Receiving data
When a WebRTC data channel message is received, onMessage method of the IDataChannelObserver is called. You can handle the received data in onMessage method as shown below.
In this example, we show the incoming text in a toast message.
Sending & receiving data with iOS SDK
Initialization
Ant Media Server and WebRTC iOS SDK can use data channels in WebRTC. In order to use the data channel, make sure that it’s enabled both server-side and mobile. In order to enable it for the server side, you can just set the enableDataChannel parameter to true in setOptions method.
WebRTC iOS SDK also provides sample code for sending and receiving messages via a WebRTC data channel.
Sending data
You can send data with the sendData method of AntMediaClient as follows.
Receiving data
When a new message is received, the delegate’s dataReceivedFromDataChannel method is called:
Take a look at the VideoViewController.swift in order to see how to use the WebRTC data channel.
Sending data with the REST method
You can also programmatically send a data channel message with REST API. Here is an example of URL usage:
You can send any text with this method. The sample command above just sends {message: "test"} to the publisher or players of the {STREAM_ID}
Receiving data channel messages with Webhook
You can programmatically collect all data channel messages for any stream with a Webhook. All WebRTC data channel messages are delivered to these hooks as well. Here is the step-by-step guide to adding a Webhook for data channel messages.
- Open your app’s
red5-web.propertieswhich is underwebapps/<app_name>/WEB-INF - Add
settings.dataChannelWebHookproperty and assign your Webhook URL. Start withhttporhttps - Save the file and restart the server.
After restarting, your webhook URL is called with data channel messages by Ant Media Server. POST method is used for sending data channel messages with “multipart/form-data” encoding. The name of the variable is the data that contains the WebRTC data channel message.
Try Ant Media Server for Free
Explore Ant Media Server now to provide viewers with a unique experience.
Try Ant Media Server for free with its full features including Flutter and other WebRTC SDKs.
We wanted to present to you a detailed article. We hope it was useful for you. We are always here for any questions you may have. You can reach us at contact@antmedia.io.
Useful Links
WebRTC SDKs’ guides for Android, iOS, React Native, and Flutter.