Unlock the full potential of your streaming platform with our in-depth guide on how to scale Ant Media Server on Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
As the demand for seamless, high-quality live streaming continues to surge, mastering the art of scalability becomes essential.
In this comprehensive post, we’ll navigate the intricacies of efficiently expanding your Ant Media Server infrastructure on GCP, ensuring optimal performance and an exceptional viewing experience for your audience.
Let’s move on to the installation.
After logging into Google Cloud Platform, create a project for yourself. We created antmedia-test for testing purposes.
Step 1: Install MongoDB Server
To create an instance in Google Cloud Platform:
Click on VM Instances > CREATE INSTANCE, and from the opened window, choose Ubuntu 22.04 as the boot disk.
Then, go to Advanced Options > Management. Add the following lines to the Automation section:
#!/bin/bash wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ant-media/Scripts/master/install_mongodb.sh && chmod +x install_mongodb.sh ./install_mongodb.sh
Click on Create to complete the process. Once the instance is created, make sure to note down its private IP address.
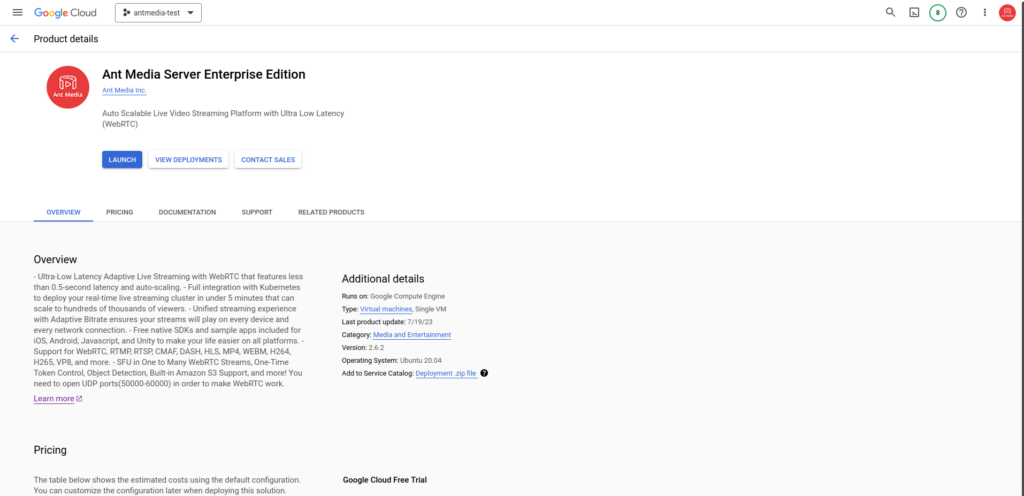
Step 2: Install Ant Media Server Enterprise Edition
To use Ant Media Server Enterprise Edition as a cluster on Google Cloud Platform Marketplace, you should first deploy Ant Media Server Enterprise Edition through the Marketplace service. Please check out this blog post to launch the AMS through the marketplace.
After the deployment process is complete, stop the instance.
Next, navigate to the Images > CREATE IMAGE tab and choose the instance you have set up as the Source disk.
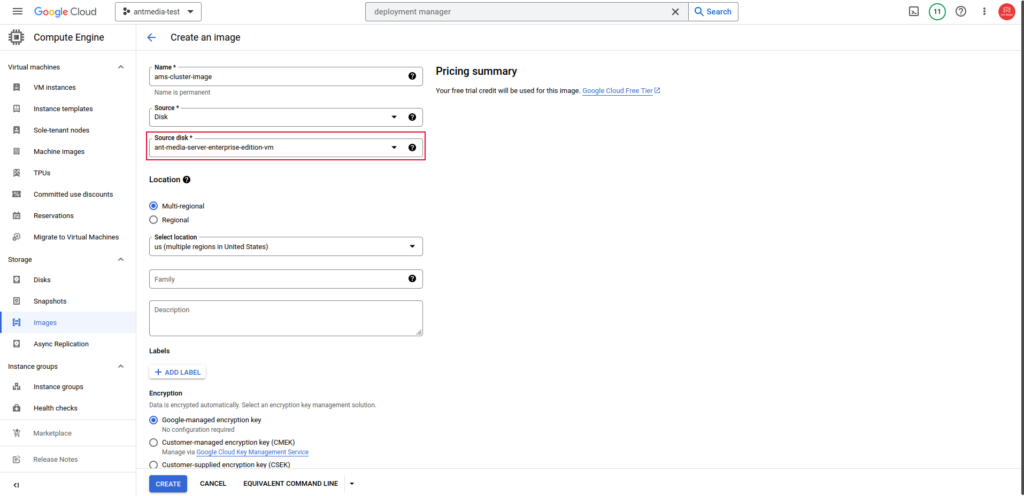
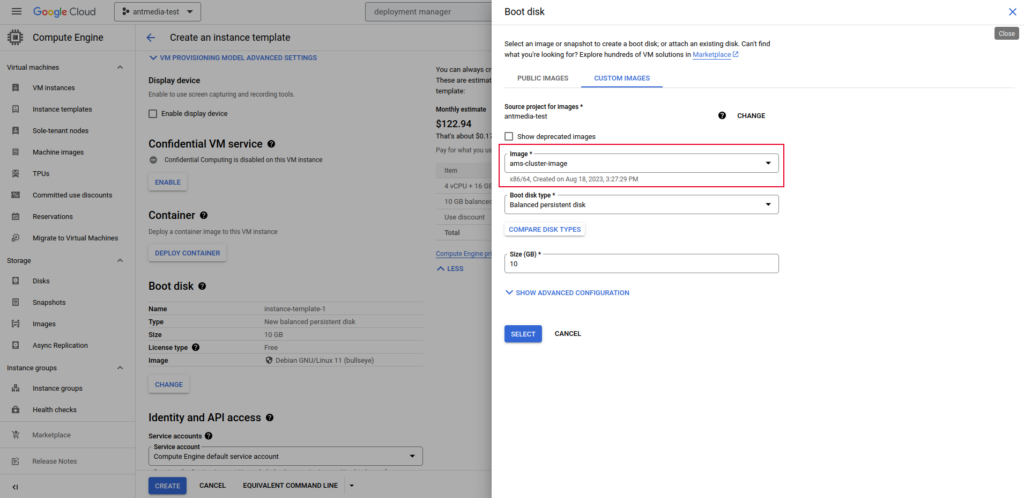
Choose Source disk for Ant Media Server on Google Cloud
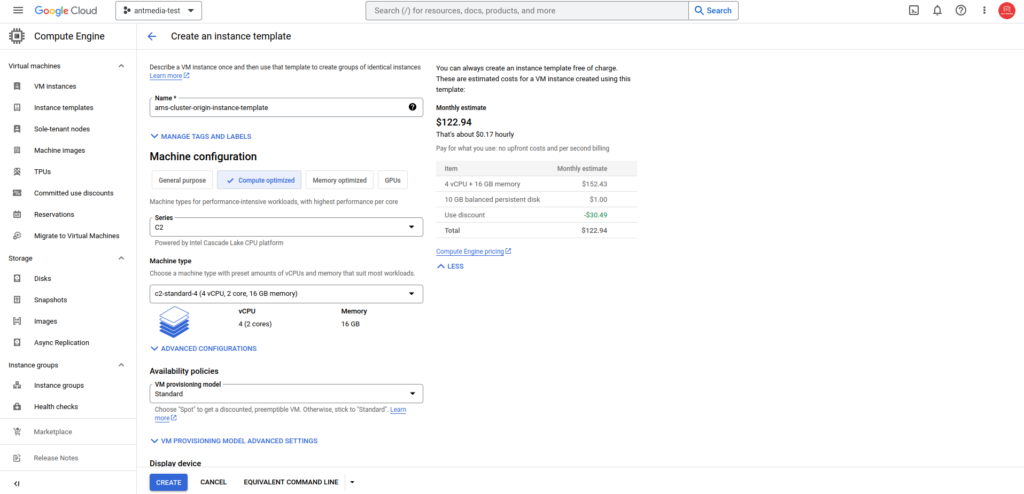
Step 3: Create an Instance Template
After the image creation process is complete, proceed to the Instance Templates > CREATE INSTANCE TEMPLATE menu.
Select the instance type
On the same screen, navigate to the Boot Disk section and click on Change > Custom Images. Then, select the image you created in the previous step.
After that, go to Advanced Options > Management Tab and add the following startup script to the Automation section:
#!/bin/bash rm -rf /usr/local/antmedia/conf/instanceId rm -rf /usr/local/antmedia/*.db.* rm -rf /usr/local/antmedia/*.db cd /usr/local/antmedia ./change_server_mode.sh cluster 10.128.0.5
In the script, please replace the private IP of your MongoDB created in Step 1. Click the Create button to create the template.
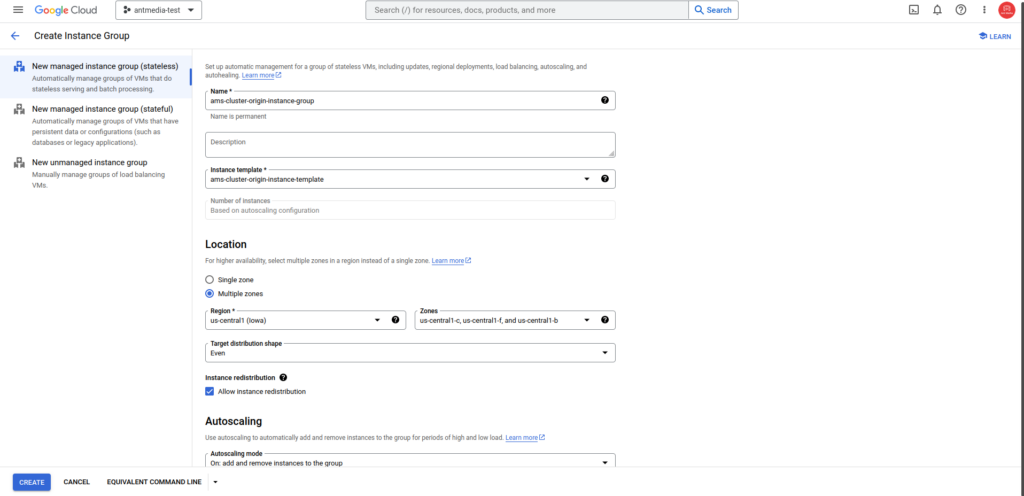
Step 4: Create the Instance group
Navigate on Google Cloud to Compute Engine > Instance Groups > CREATE INSTANCE GROUP. Then, select the name and template as shown in the screenshot, and choose Multiple Zones for the Location.
For auto-scaling, specify the minimum and maximum instance counts you want to set up, then configure the CPU Utilization to 60% and click on the Create button.
Then repeat the same process for the Edge group as well.
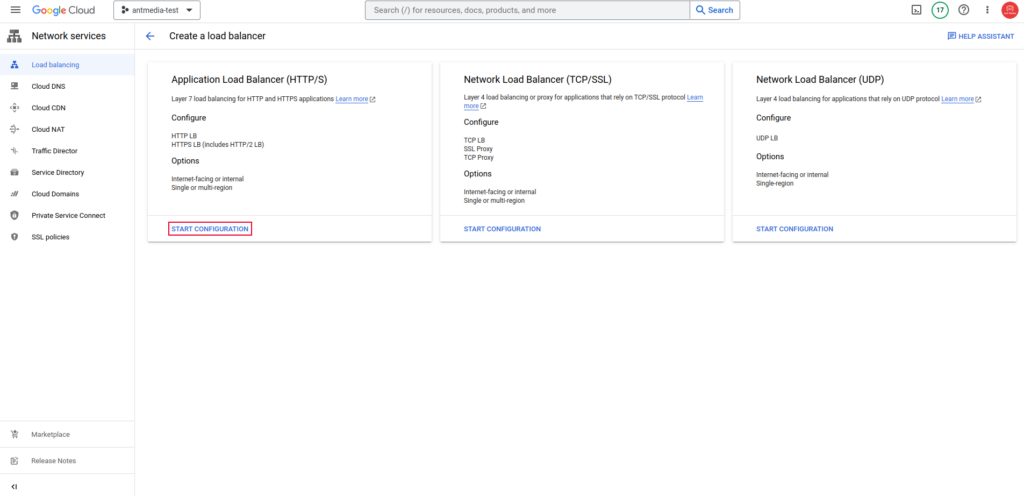
Step 5: Create a Load Balancer
The autoscaling groups are now created. Let’s move on to configuring the Load Balancer to distribute the load.
In the search bar, type “Load Balancer” and open the “Load balancing” service, then click on CREATE LOAD BALANCER and select Application Load Balancer.
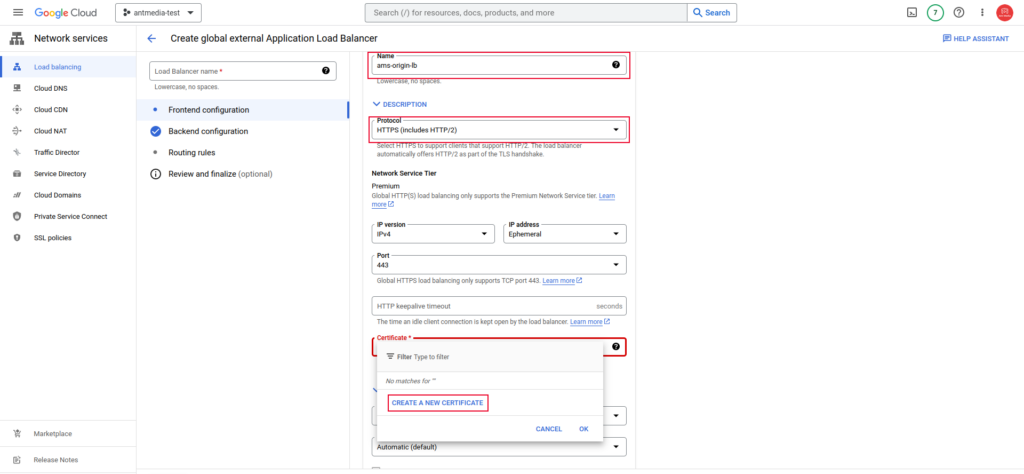
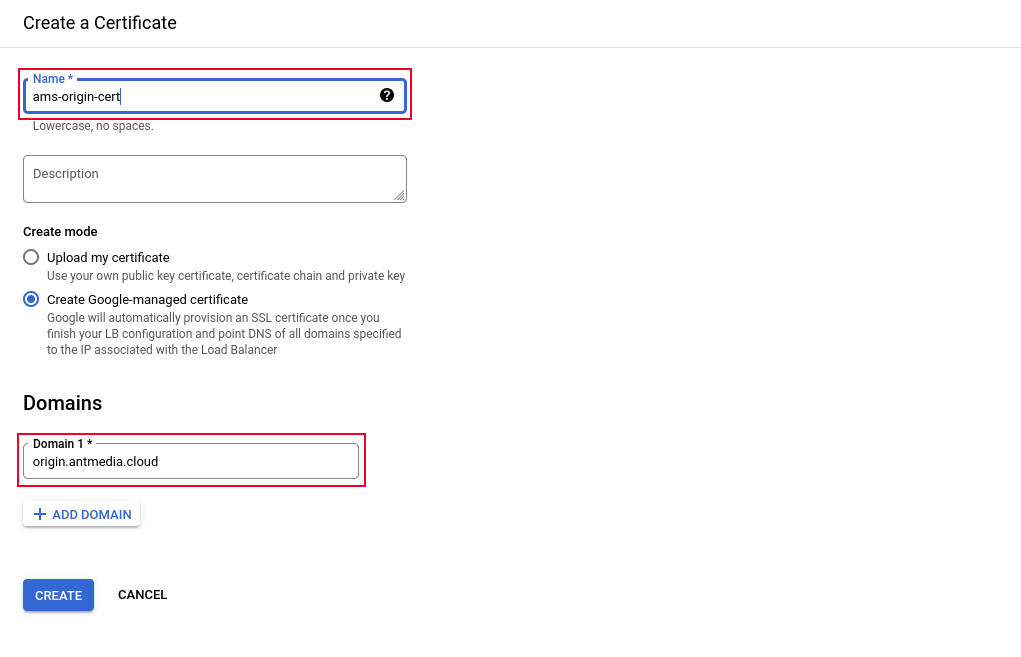
In the Load Balancer menu, after selecting the Name and Protocol, go to the certificate section and create a new certificate by choosing “CREATE A NEW CERTIFICATE.”
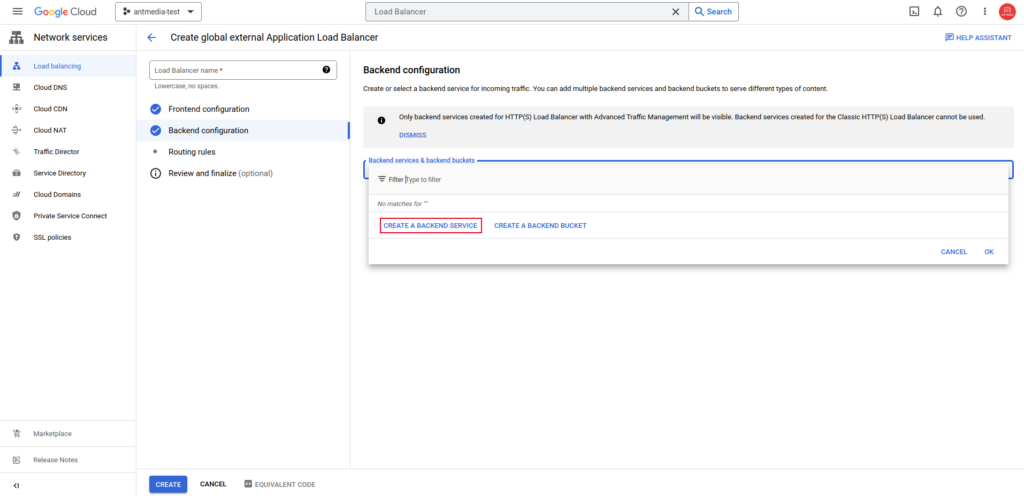
Then, fill in the required fields and create the certificate. You can also use your own SSL certificate by uploading it. After that, click on the “Backend configuration” section.
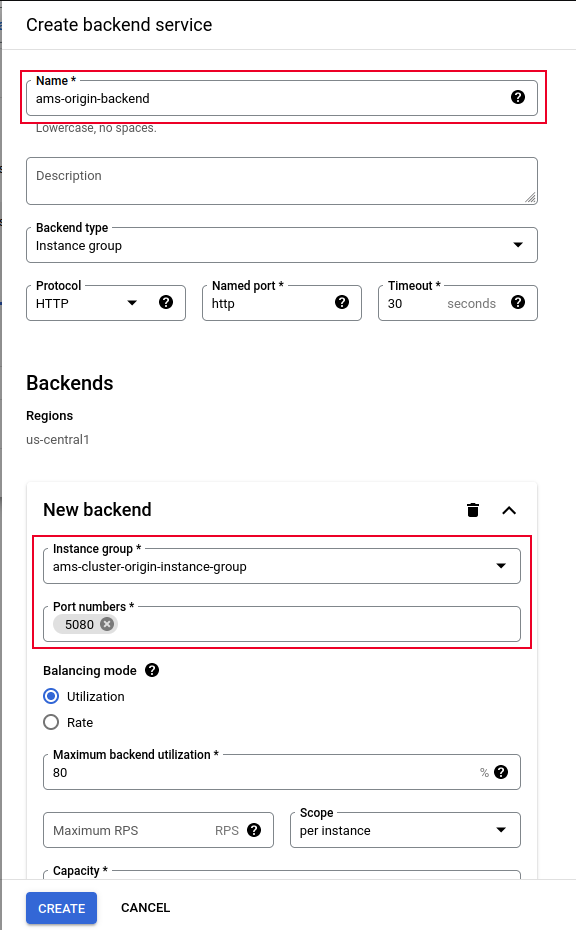
In the upcoming screen, we will create the Backend Pool (both Origin and Edge) and Health Check.
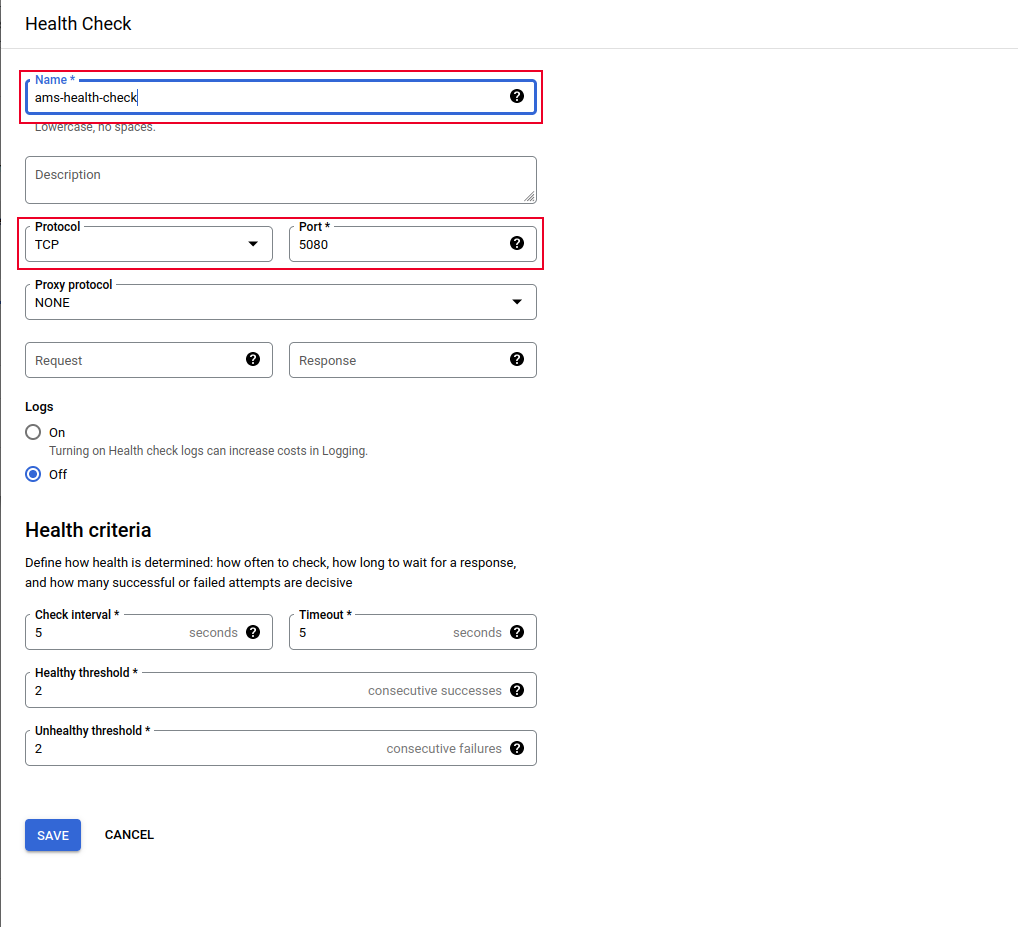
In the same backend configuration, to create the Health Check configuration, click on Health Check > CREATE HEALTH CHECK and add it as shown below:
Click on Create to finalize the configuration for both the Backend and the Health check. Then, click Create again to complete the Load Balancer configuration.
Repeat these steps for the Edge side as well.
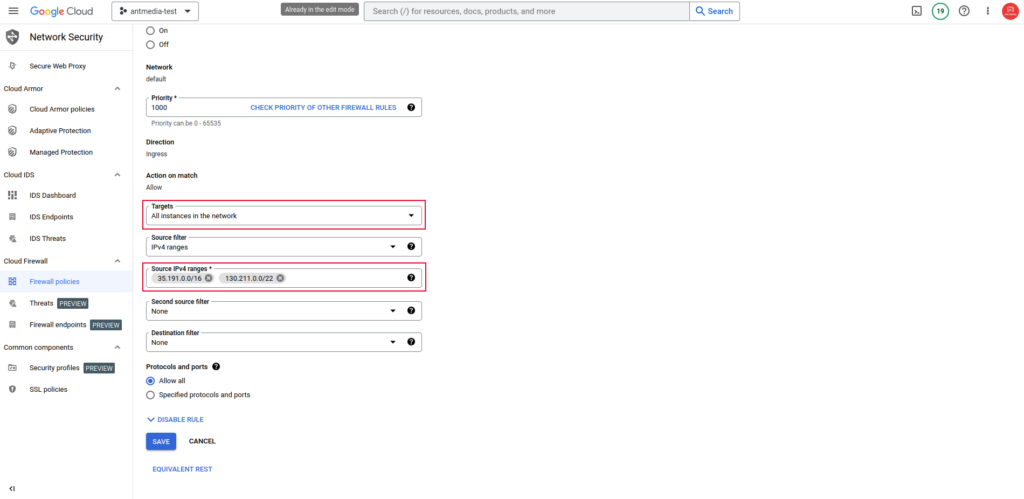
Note: If the Load Balancers cannot access the Backend servers, you should add a firewall rule as shown below.
Go to VPC Network > Firewall > Create firewall Rule and add the rule as shown below. Now the load balancer should be able to access the Ant Media Server Backend servers.
You can allow all IPs by adding the 0.0.0.0/0 CIDR block if required.
How to set up Firewall policies on Google Cloud?
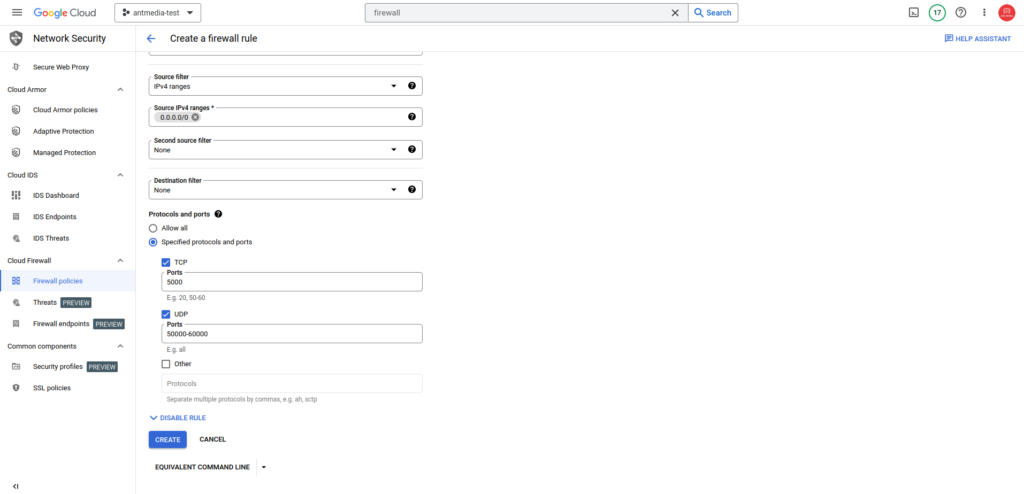
Step 6: Configure Firewall rule for Ant Media Servers
For TCP port 5000 and UDP ports 50000–60000, go to VPC Network > Firewall > Create firewall rule and add the rule as shown in the image below.
Finally, in your DNS management, define the IP addresses of both the origin and edge load balancers.
That’s it! You’re all set. You can now access the Ant Media Server servers to publish, and play the streams using either the origin or edge group.